
How AI Predicts Customer Behavior
AI helps businesses predict customer behavior by analyzing patterns in data like purchases, support tickets, and engagement metrics. This allows companies to act before issues arise, such as preventing churn or identifying upsell opportunities. Key applications include:
- Churn Prediction: Identifying customers likely to leave and enabling targeted retention efforts.
- Upsell and Cross-Sell: Recommending products or services based on purchase history and behavior.
- Engagement Monitoring: Detecting declining activity to re-engage customers effectively.
For example, a subscription service reduced churn by 20% with AI-driven strategies, while an online retailer boosted sales by 15% through improved recommendations. AI integrates with tools like CRMs to deliver actionable insights, streamlining workflows and improving customer interactions. To succeed, businesses must focus on clean data, clear goals, and continuous monitoring to refine models and ensure compliance with privacy laws.
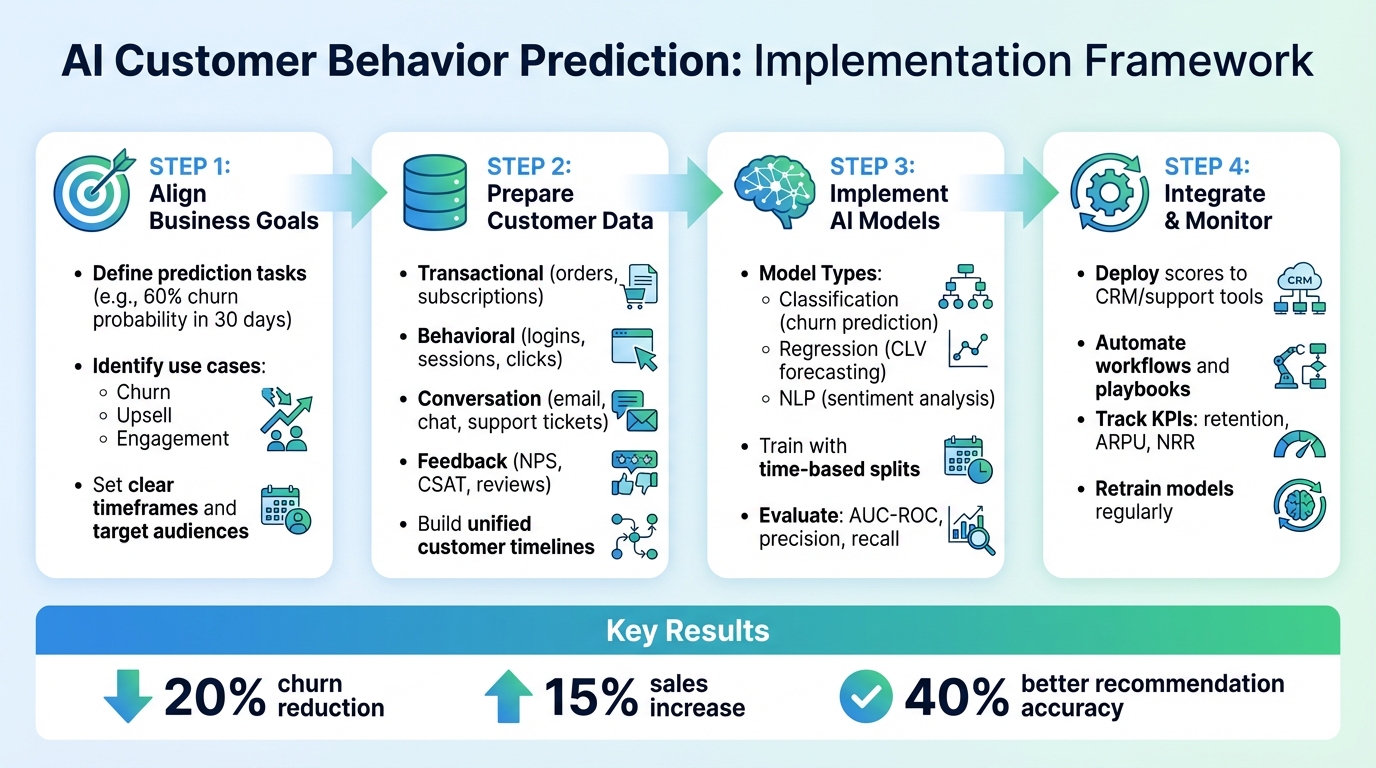
4-Step Framework for Implementing AI Customer Behavior Predictions
How to predict customer behavior without a data science team
Aligning Business Goals with AI Predictions
Before diving into building an AI model, the first step is to translate your business goals into clear, actionable prediction tasks. For example, a broad objective like "reduce churn" can be reframed as an AI task: predicting which active subscribers have more than a 60% chance of canceling within the next 30 days based on factors like usage patterns, support tickets, and payment history. Similarly, a goal such as "increase average order value (AOV) by $10" might focus on identifying customers who are likely to accept cross-sell or upsell offers during checkout or in an upcoming email campaign. To make this process effective, define the timeframe, target audience, and specific actions (like offering discounts, personalized outreach, or tailored recommendations). This structured approach ensures that your business goals align seamlessly with AI predictions and the actions your team will take.
Finding Key Use Cases: Churn, Upsell, and Engagement
AI predictions can be particularly impactful in three key areas:
- Churn Prediction: AI models classify customers based on their likelihood of canceling or halting purchases within a specific timeframe. This allows businesses to launch proactive retention efforts. For instance, an apparel subscription service used churn prediction to guide retention strategies, leading to measurable improvements.
- Upsell and Cross-Sell Prediction: These models analyze purchase histories, browsing behavior, and customer similarities to recommend the next best offer. One e-commerce retailer used AI to predict add-on purchases, significantly improving recommendation accuracy and boosting sales.
- Engagement Risk and Reactivation: By identifying users who show declining engagement - like fewer logins, reduced email opens, or less interaction with support - AI can help businesses design targeted reactivation campaigns. In one example, combining real-time and historical engagement data led to a 15% increase in sales through optimized reactivation efforts.
Each of these use cases should tie directly to actionable workflows. In marketing, churn scores can determine which customers receive loyalty perks or win-back offers before their subscriptions expire. For upselling, AI can suggest premium bundles in emails or personalize on-site recommendations. In customer support, AI can flag at-risk users based on sentiment analysis or recurring issues, enabling faster resolutions through escalations or proactive follow-ups. Tools like Inbox Agents can even route high-churn-risk customers to senior representatives while using AI-generated summaries and smart replies to improve response times and satisfaction. In sales, account managers can prioritize outreach to accounts at risk of leaving or identify those with strong potential for expansion.
Ranking Use Cases by Revenue Impact and Data Availability
Not all use cases are created equal. Before committing resources to model development, evaluate potential projects based on four key factors: revenue impact, actionability, data quality and availability, and operational complexity. The most valuable use cases tend to offer a strong revenue boost, clear next steps, reliable data, and manageable implementation challenges - like churn prediction for subscription services or upsell recommendations in e-commerce.
A straightforward way to prioritize use cases is to estimate their potential annual impact. For instance, a SaaS company with $500,000 in monthly recurring revenue (MRR) and a 4% monthly churn rate could retain an additional $4,000 in MRR by reducing churn to 3.2% (a 20% relative improvement). Over a year, the compounded benefits would be substantial. Similarly, an online retailer processing 100,000 monthly orders with an $80 AOV could generate an extra $100,000 in monthly revenue by increasing AOV by just $5 on 20% of orders.
Data quality and availability are also crucial when deciding which use cases to tackle first. Projects that rely on well-organized, historically logged events - like purchases, cancellations, renewals, ticket closures, or email interactions - are quicker to develop and validate. Auditing historical data ensures that key timestamps, customer IDs, and outcomes are consistently captured across channels like web, app, email, SMS, and phone. By integrating these data sources into a unified customer view, businesses can significantly enhance the accuracy of engagement and churn predictions, setting the stage for more effective AI-driven strategies.
Preparing Customer Data for AI Predictions
After identifying your key use cases, the next big step is getting your data ready for AI models. High-quality, consistent data is essential for accurate predictions. Centralizing all customer interactions - actions, feedback, sentiments, and more - into a unified view is the foundation.
Key Data Sources for Customer Behavior Analysis
To build effective AI predictions, you’ll need data from four main categories. First up is transactional data, which includes order IDs, product details, prices (e.g., $1,234.56), and subscription events. Then there’s behavioral data, which tracks how customers engage digitally - think add-to-cart actions, logins, session durations, app feature usage, and interactions with emails or push notifications.
Conversation data is another critical piece. This covers interactions across email, SMS, live chat, voice calls, and platforms like WhatsApp or Instagram. You’ll want to capture timestamps (MM/DD/YYYY, 12-hour format), sender types, response times, and resolution outcomes. Tools like Inbox Agents can consolidate these conversations into one interface, summarize them, and even assign sentiment scores for easier integration into your AI models.
Finally, there’s feedback data, which offers direct insights into customer satisfaction. This includes NPS and CSAT survey results, in-app ratings, review scores and text from app stores or e-commerce sites, support ticket surveys, and social media sentiment. By combining these four data types, you get a complete picture of the customer journey, which greatly improves predictions for churn and engagement.
Building Unified Customer Timelines
To make sense of all this data, you’ll need to create a single, time-ordered timeline for each customer. Start by centralizing raw data into a warehouse using customer IDs and timestamps. A crucial step is normalizing keys - link every record to a single customer ID across CRM, billing, product, and support systems. Use rules like matching email addresses and the last four digits of payment cards to merge duplicates.
Next, establish a common event schema with fields like customer_id, event_type (e.g., PURCHASE, CART_ABANDON, CHAT_MESSAGE, NPS_RESPONSE), event_timestamp_utc, amount_usd, channel, and metadata. Store timestamps in UTC for modeling but display them in US-friendly formats (MM/DD/YYYY, 2:30 PM) in dashboards for business users. Arrange all events chronologically to form a timeline - this sequence is essential for advanced models like LSTMs, which are particularly good at predicting churn and next actions. Add key event markers, such as first purchases, support tickets, negative reviews, or subscription changes. Spot-check timelines to ensure events are in the correct order and no key data is missing. Once the timelines are clean, you can start extracting features for your AI models.
Feature Engineering for AI Models
Features extracted from unified timelines are the backbone of AI predictions. For churn prediction, focus on recency metrics, like days since the last purchase or login - these often correlate with churn. Frequency metrics, such as the number of purchases or sessions in the last 30, 60, or 90 days, can reveal engagement levels. Monetary metrics, including total spend over the past 3, 6, or 12 months, average order value, and lifetime value, help prioritize high-value customers.
Behavioral features might track session counts, average session lengths, pages per session, or conversion rates like cart-to-purchase ratios over time. A sudden drop in these can signal disengagement. From conversation data, you can derive metrics like average response times, interaction volumes (number of conversations and messages per conversation), and issue categories (e.g., billing or technical problems). Sentiment analysis, which assigns values from -1 to +1 to customer messages, can also be aggregated to track overall sentiment, with sustained negativity often linked to churn.
For feedback data, use raw scores like NPS (0–10) and CSAT (1–5) and categorize them (e.g., NPS promoters 9–10, passives 7–8, detractors 0–6). Create features like recent NPS scores, CSAT trends, last survey dates, and counts of negative reviews. Add temporal features like day of the week, hour of the day (0–23), weekends versus weekdays, US holidays, and local time zones to predict when customers are most likely to respond or convert. Document all features in a data dictionary, detailing their source, description, type, and transformation process. Keep an eye on data drift metrics to identify when distributions shift and retraining is needed.
Implementing AI Models for Customer Predictions
Once you have clean, feature-rich customer data, the next step is choosing the right AI model. With your data prepared and features engineered, it's time to build models that can predict customer behavior. The key is to match the model to your specific business goals and train it effectively to ensure the predictions are accurate and actionable.
Selecting the Right AI Models for Specific Use Cases
Different business goals call for different types of AI models. For churn prediction, where the objective is to determine whether a customer will stay or leave, classification models are a good fit. Logistic regression is a great starting point due to its simplicity and interpretability. If you need more advanced options, consider models like random forests, XGBoost, or LightGBM. These gradient-boosted tree models often strike a balance between speed and accuracy, making them ideal for churn scenarios.
When it comes to predicting customer lifetime value (CLV) or future spending, regression models are more suitable. These models output dollar values, capturing insights from purchase history, engagement patterns, and other monetary features. Options include linear regression, gradient boosting regression, or even deep learning models for more complex relationships. For next best offer recommendations, collaborative filtering and matrix factorization are excellent tools to uncover customer behavior patterns.
If timing and sequences are critical - like forecasting weekly active users or predicting a customer's next purchase - time-series models such as ARIMA, Prophet, or sequence models like LSTMs and Transformers can be highly effective. These models analyze the order of events in your data, identifying trends that static models might overlook.
For conversation-driven businesses, natural language processing (NLP) models are invaluable. Sentiment classifiers, intent detectors, and topic models can process customer interactions like emails, chat messages, and support tickets to extract actionable insights. These insights - such as identifying frustration or upgrade interest - can feed into churn and upsell models. Tools like Inbox Agents can integrate NLP capabilities directly into messaging workflows, enabling features like smart replies, prioritizing at-risk customers, and personalizing responses across email, SMS, and social platforms.
Once you've selected a model type aligned with your goals, the focus shifts to training and validating the model.
Training and Evaluating AI Models
Start by defining a target label that reflects real business outcomes. For instance, you might label a customer as churned if they show no activity or payments for 60 days, but you can adjust this timeframe based on your billing cycles and customer behavior. It's critical that the labels accurately represent your business realities.
When splitting your data, use time-based splits rather than random sampling. Train your model on earlier data, validate it on more recent periods, and test it on the latest data to mimic real-world deployment. For US businesses, consider including seasonal trends like Black Friday or holiday shopping spikes so the model learns these patterns instead of misinterpreting them as anomalies.
To evaluate churn models, use metrics like AUC-ROC, precision, and recall. Since churn is often a rare event, precision-recall curves can help set appropriate thresholds for interventions. For example, one marketplace that incorporated real-time browsing data improved recommendation accuracy by 40%, leading to a 15% boost in sales.
For CLV and spending predictions, focus on metrics like mean absolute error (MAE) and root mean squared error (RMSE) to gauge how close your predictions are to actual values. Always translate these metrics into business terms. For example, consider how a 5-point increase in recall might impact monthly recurring revenue or how better upsell ranking could raise the average order value. In one case, Trendy Butler used churn prediction models built on behavioral data to improve customer retention by 20% through proactive outreach to at-risk subscribers.
To finalize your model, address potential pitfalls like data leakage and class imbalance. Prevent data leakage by ensuring the model only uses information available at prediction time - exclude future data or outcome indicators. Handle class imbalance, where churners are often a small minority, by applying techniques like class weighting, oversampling the minority class, or adjusting decision thresholds. Regularly check for label bias to ensure the outcomes align with actual business results. Document your labeling process, maintain reproducible workflows, and version your data and code to support audits and future updates to the model.
sbb-itb-fd3217b
Integrating AI Predictions into Customer Workflows
Once models are trained and predictions are ready, the real challenge is embedding these insights into everyday workflows. The real value of AI predictions emerges when they seamlessly integrate into tools like CRMs or messaging platforms. By connecting predictions to these systems, businesses can turn data into actionable steps that drive results.
Deploying Prediction Scores in CRM and Support Tools
One effective way to use prediction scores is by adding them as fields in customer records within tools like Salesforce, HubSpot, Zendesk, or Intercom. Fields such as Churn Risk Score, Next Best Offer, or Engagement Tier can be updated daily through APIs, ensuring teams always have the latest insights at their fingertips. For example, a clear visual indicator - like a red flag for "At Risk" customers - can help support agents and sales reps quickly spot critical situations.
Customizing list views and queues can further enhance productivity. Support agents might filter for "high churn risk customers with unresolved tickets", while sales teams could prioritize customers with a high likelihood of upselling and an upcoming contract renewal. For U.S.-based teams, displaying customer lifetime value in the familiar dollar format (e.g., $12,500) ensures consistency and clarity.
To make these scores actionable, map them to specific playbooks. For instance, a score above 0.8 might trigger immediate, personalized outreach, while lower scores could lead to standard follow-ups. High-value customers might be routed to senior agents for VIP treatment, complete with faster response times. Automating these workflows within CRMs - like creating tasks when a Churn Risk Score exceeds 0.8 - ensures timely action. A real-world example comes from Trendy Butler, a subscription service that used churn prediction models to implement preemptive outreach, boosting retention by 20%. These integrations close the gap between predictive insights and practical customer engagement.
Using AI Predictions in Conversation Management
AI predictions can also enhance how teams manage customer conversations. Platforms like Inbox Agents can integrate prediction scores with real-time data to prioritize critical messages. This ensures that urgent issues are addressed promptly, often within minutes instead of hours.
Beyond prioritization, AI can shape the tone, content, and offers in automated replies. For instance, if a high-risk customer has repeated complaints, the system could suggest a tailored response that acknowledges their frustration and offers a retention incentive, such as a discount or an upgraded plan. It might also recommend escalating the issue to a human agent for a more personal touch. On the other hand, for engaged customers with high upsell potential, AI could suggest actions like recommending add-ons or higher-tier plans.
AI can even assist with negotiation strategies. For example, by analyzing predicted customer lifetime value and sensitivity to discounts, the system might suggest offering up to 15% off an annual plan priced at $299.00 for a specific customer segment. This keeps offers attractive while maintaining profitability. These workflows ensure that AI predictions aren't just numbers - they drive smarter, more personalized customer interactions.
Measuring the Impact of AI-Driven Predictions
To gauge the success of AI integration, track key metrics such as retention rates, churn rates, net revenue retention (NRR), and average revenue per account (ARPA). Operational metrics like first response times, resolution times, and first contact resolution rates are also crucial. Additionally, monitor customer satisfaction through CSAT and NPS scores to ensure automation enhances, rather than diminishes, the customer experience.
A/B testing can provide further validation. For example, compare outcomes between a control group using traditional processes and a treatment group leveraging AI-enhanced workflows, such as prediction-driven playbooks or smart replies. For churn models, focusing interventions on the top 20–30% of high-risk customers and comparing results with a holdout group can reveal the true impact of these efforts. This data-driven approach ensures that AI integrations are both effective and measurable.
Monitoring and Refining AI Prediction Systems
Building an AI model is just the starting point. Over time, models can lose their effectiveness due to changes in customer behavior, market dynamics, or economic conditions. This phenomenon, known as data and concept drift, requires ongoing attention to keep your AI systems performing well.
Tracking Model Performance and Business KPIs
To ensure your AI model continues to deliver, track core metrics such as AUC, precision, recall, and calibration error. Automated dashboards can help by flagging issues, such as a drop in AUC by more than 0.05 or significant shifts in the average churn probability - anything beyond two standard deviations from the historical mean.
In addition to technical metrics, keep an eye on business KPIs like monthly churn rate, customer lifetime value (CLV), average revenue per user (ARPU), and upsell conversion rates. For revenue-based KPIs, express values in USD (e.g., incremental revenue per at-risk customer saved) and monitor trends using the MM/DD/YYYY date format. A/B testing is a must to validate the effectiveness of model-driven actions. For example, compare retention rates and revenue between customers who received AI-driven outreach and those in a control group.
Data drift can also undermine your model. Regularly compare incoming feature distributions - like login frequency, ticket volume, or purchase amounts - against your training baseline using statistical tests. For instance, if your model was trained on pre-holiday shopping behavior but is now scoring post-holiday data, predictions might be off. Plan monthly reviews and quarterly deep-dives to determine when to pause deployment, investigate data pipelines, or retrain the model.
These ongoing evaluations lay the groundwork for the updates discussed below.
Retraining Models and Addressing Bias
Retraining your model should be a regular practice. For high-volume B2C scenarios, this might mean monthly or weekly updates, whereas B2B contexts may only require quarterly adjustments. Major events - like product launches or economic shifts - or a significant drop in AUC or data drift beyond acceptable limits also signal the need for retraining.
When retraining, use the most recent 6–12 months of data and split it into training, validation, and test sets, keeping the temporal order intact to avoid data leakage. For example, train on data through June 30, 2025, validate on July, and test on August data. Test new models in shadow mode to assess live performance without affecting real-world decisions. Only promote the updated model if it outperforms the current version in both predictive quality and business outcomes - and meets privacy and fairness standards.
Bias is another critical issue to address. Disparities can arise if certain groups - based on demographics, channels, or customer segments - are consistently flagged as higher risk for churn or receive fewer upsell opportunities. Analyze predicted scores and outcomes by sensitive attributes (where legally allowed) or proxies like ZIP code–level socioeconomic data. Compare false positive and false negative rates, as well as precision and recall, across groups to identify systemic issues. If disparities are detected, consider adjusting your training datasets, modifying how sensitive attributes are used, or implementing fairness-aware algorithms. Establish a bias review committee to regularly audit models, document trade-offs, and approve significant updates.
Ensuring Compliance with Privacy Regulations
Once performance and fairness are addressed, compliance with privacy laws is essential. In the United States, regulations like the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA), HIPAA (for health data), and GLBA (for financial data) set strict guidelines. These laws give consumers the right to know what personal data is collected, access it, request deletion (with some exceptions), and opt out of data sharing. For AI predictions, this means clearly disclosing how customer data - such as purchases, interactions, and behavioral logs - is used, obtaining explicit consent when required, and honoring opt-out requests.
Privacy notices and support channels for data access or deletion must be easy to find and meet response deadlines, typically 45 days under CCPA. Adopt data minimization practices by collecting only what's necessary for predictions, and secure data with measures like encryption (in transit and at rest), access controls, and auditing. To further reduce privacy risks, consider techniques such as aggregation, pseudonymization, federated learning, or synthetic data generation.
For tools like Inbox Agents, which unify messaging channels and provide AI-driven summaries and smart replies, apply the same stringent privacy and security standards to conversation data. This ensures both compliance and user trust.
Conclusion
After preparing your data, implementing AI, and integrating it seamlessly into your workflows, the next step is using these tools to reshape how you manage customer relationships. AI takes customer behavior prediction to a whole new level by leveraging data to deliver precise, actionable insights. By analyzing behavioral patterns, transactional history, and interaction data, businesses can anticipate churn, uncover upsell opportunities, and enhance engagement, enabling teams to take proactive steps.
A practical starting point? Focus on a single, high-impact use case - like reducing subscription churn or recovering abandoned carts. Centralize customer data from all channels and integrate predictive scores into your CRM, marketing, and support tools. Platforms like Inbox Agents make this easier by embedding features like churn risk alerts, smart replies, and personalized outreach directly into the tools your teams already use. When AI insights are accessible in day-to-day workflows, they transform from theoretical concepts into practical solutions.
The benefits are tangible. Case studies and real-world applications demonstrate AI’s ability to improve retention and drive upsell success.
To maintain long-term effectiveness, continuous monitoring, regular model retraining, and strict adherence to privacy standards are essential. Businesses that embrace AI to predict customer needs and deliver tailored experiences are gaining a competitive edge. The real question isn’t whether to adopt AI for customer behavior prediction - it’s how quickly you can implement it, test its impact with A/B experiments, and scale successful strategies while ensuring trust and compliance.
FAQs
How does AI help businesses retain customers?
AI empowers businesses to keep their customers by studying behavior patterns to spot signs of churn and identify chances for meaningful engagement. By offering customized interactions and enabling proactive communication, AI strengthens customer connections and builds loyalty.
Tools like Inbox Agents make it easier to manage communication across different platforms, automate quick responses, and deliver personalized experiences. These AI-driven capabilities ensure smooth and consistent interactions, helping businesses retain customers, lower churn rates, and focus on their most valuable clients.
What types of data does AI use to predict customer behavior?
AI depends on a range of data to accurately anticipate customer behavior. Some of the key factors it examines include message content, interaction history, response times, engagement trends, and customer preferences. By digging into these details, AI can identify patterns that hint at potential customer churn, upsell opportunities, or ways to boost engagement.
When information from various messaging platforms - such as email, social media, and chat apps - is combined, AI gets a fuller picture of how customers interact. This broader perspective allows businesses to make more accurate predictions and offer personalized, timely responses, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
How can businesses ensure their AI predictions follow privacy regulations?
To align AI predictions with privacy regulations, businesses need to implement strict data governance policies and secure explicit user consent before gathering or analyzing any data. It's equally important to anonymize customer information and comply with regulations such as GDPR and CCPA.
Conducting regular audits and openly sharing details about how data is used can enhance transparency and accountability. By focusing on these practices, companies not only stay compliant but also foster trust and uphold ethical standards in AI operations.
