
How AI Bias Impacts Customer Journey Mapping
AI bias can distort customer experiences, leading to unfair treatment of certain groups. This can harm brand trust, reduce customer satisfaction, and even result in lost revenue. Here’s what you need to know:
- AI Bias in Action: Algorithms may prioritize certain customer groups over others due to data or design issues. For example, premium offers might favor high-income users, while others get limited options.
- Key Types of Bias:
- Data Bias: When training data lacks diversity or reflects historical prejudices.
- Algorithmic Bias: Flaws in model design that lead to unequal outcomes.
- Operational Bias: Insufficient oversight during AI deployment.
- Consequences: Biased systems can misinterpret behavior, exclude groups, and reduce trust. Examples include inaccurate recommendations or discriminatory lending decisions.
- Solutions:
- Use diverse, high-quality data.
- Build transparent models with fairness constraints.
- Regularly audit AI systems for bias.
- Employ platforms with built-in bias controls.
To reduce AI bias, businesses need to focus on data quality, model transparency, and continuous monitoring. This ensures fairer, more accurate customer interactions while meeting regulatory and ethical standards.
Where Does Customer Journey Mapping Go Wrong? (And How to Fix It)
What is AI Bias and How Does it Affect Customer Journey Mapping?
Three Types of AI Bias in Customer Journey Mapping
Understanding AI Bias in Customer Journey Mapping
AI bias refers to systematic errors that lead to unfair treatment of certain customer groups. These errors can arise from issues in training data, how algorithms are designed, or how they are used in practice. In the context of customer journey mapping, bias can show up when AI misinterprets customer behavior, overlooks specific groups, or treats similar customers differently.
For instance, if rural or low-income customers are underrepresented in datasets, AI might fail to accurately reflect their experiences. This can result in biased customer journey maps that misguide engagement strategies. Businesses may end up focusing on well-represented groups while neglecting others. Let’s dive into the specific types of bias that can skew these maps.
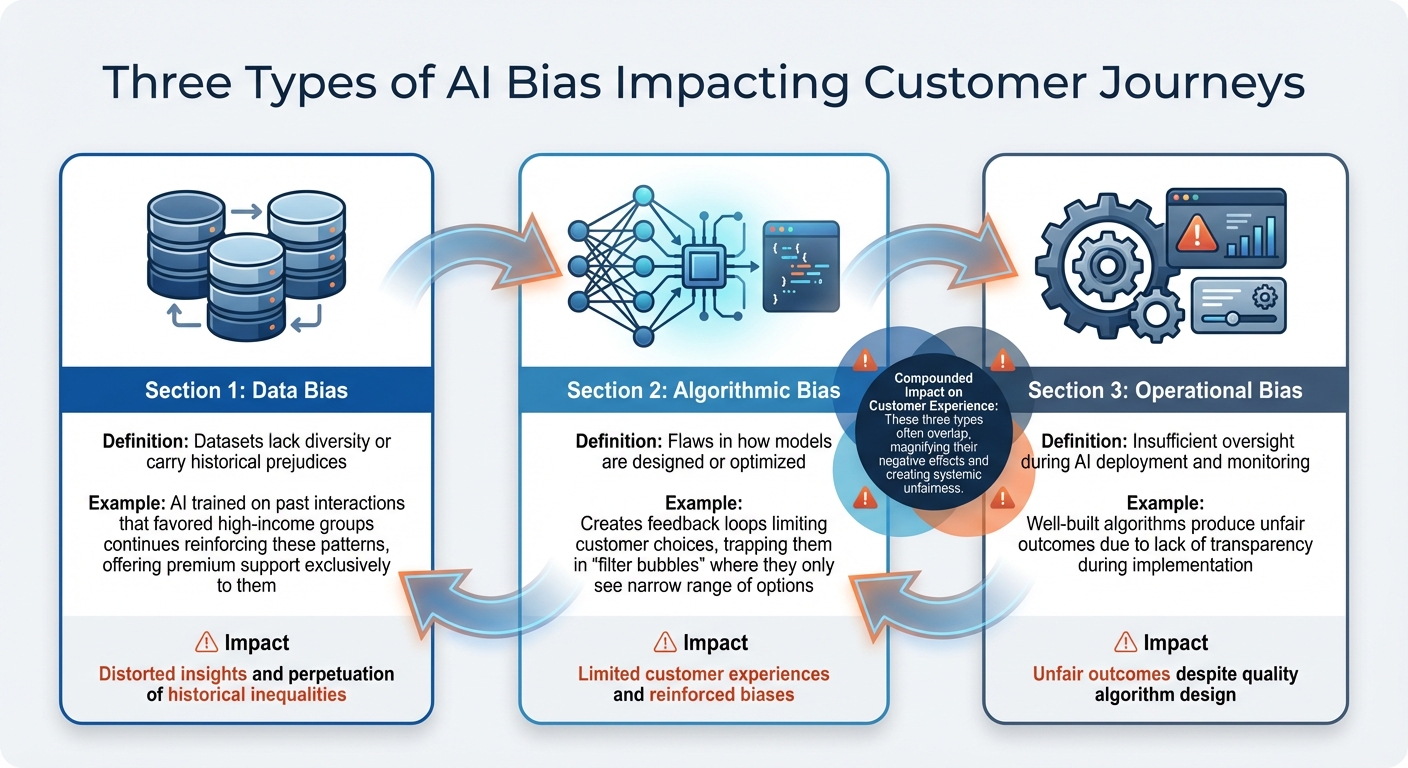
Types of AI Bias Impacting Customer Journeys
Three key types of bias can disrupt AI-driven customer journey mapping:
- Data bias happens when datasets lack diversity or carry historical prejudices. For example, if an AI system is trained on past customer interactions that favored high-income groups - such as offering premium support exclusively to them - it might continue reinforcing these patterns, leading to distorted insights.
- Algorithmic bias emerges from flaws in how models are designed or optimized. This can create feedback loops that limit customer choices, trapping them in "filter bubbles" where they only see a narrow range of options.
- Operational bias arises from how AI is implemented and monitored. Even well-built algorithms can produce unfair outcomes if there’s insufficient oversight or transparency during deployment. Often, these biases overlap, compounding their impact on the customer experience.
Together, these biases not only skew data interpretation but also damage the trust customers place in a brand.
The Damage AI Bias Can Do to Customer Trust and Experience
AI bias can seriously harm customer trust by creating interactions that feel unfair or overly intrusive. When personalization crosses the line into invasiveness, it can erode both trust and satisfaction. In these situations, customers often blame the brand itself, not the technology behind it.
Biased journey maps can lead to irrelevant recommendations or unfair treatment, which undermines customer loyalty. For instance, retargeting ads for items a customer has already purchased or pricing discrepancies based on demographic factors can make customers feel alienated. This sense of unfairness not only reduces satisfaction but can also drive customers away - especially in an era where fairness and privacy are non-negotiable for many consumers.
Examples of AI Bias Distorting Customer Journeys
AI bias can significantly disrupt customer journeys, affecting key touchpoints and leading to real-world consequences. Let’s explore how this unfolds at different stages.
During the awareness and discovery stage, facial recognition systems have shown troubling disparities. Joy Buolamwini's Gender Shades project uncovered that commercial facial recognition systems had error rates as low as 0.8% for light-skinned males, but those rates soared to 34.7% for dark-skinned females. To put it another way, while these systems misidentified the gender of only 1% of white men, they misclassified up to 35% of Black women. In a retail context, this kind of bias can result in inaccurate or irrelevant messaging during a customer’s very first interaction. This flawed starting point often sets the tone for additional biases throughout the customer journey.
Bias is also evident in hiring and recruitment, a crucial stage for customer-facing organizations. A University of Washington study in October 2024 examined three large language models used for resume ranking. The findings were stark: these models favored white-associated names 85% of the time, compared to just 9% for Black-associated names. Similarly, male-associated names were favored 52% of the time, while female-associated names received preference only 11% of the time. This means qualified candidates are often passed over before their applications even reach a human recruiter, highlighting how AI bias can infiltrate and distort customer-related processes.
The risk assessment and decision-making stages are no exception. A 2016 ProPublica investigation revealed that the COMPAS algorithm, used in criminal justice, labeled Black defendants as high-risk 45% of the time, compared to 23% for white defendants. Similar patterns have been observed in financial services, where AI systems rely on proxy variables like ZIP codes or surnames to infer race. This practice has led to discriminatory lending decisions, effectively shutting entire communities out of access to credit or favorable loan terms.
These examples demonstrate that focusing solely on overall accuracy can lead to unbalanced error rates. The result? Customers may be denied loans, shown irrelevant recommendations, or unfairly excluded from opportunities - all consequences of unchecked AI bias.
sbb-itb-fd3217b
How to Reduce AI Bias in Customer Journey Mapping
Addressing AI bias in customer journey mapping requires intentional strategies at every step. By taking deliberate actions, businesses can create AI systems that reflect fairness and accuracy. Here are some practical steps to consider.
Improving Data Quality and Representation
The accuracy of AI systems starts with the data they are trained on. High-quality, diverse datasets are essential. As IBM explains:
Machine learning trained on the wrong data will produce wrong results. Whatever data is fed into the AI should be complete and balanced to replicate the actual demographics of the group being considered.
To build a well-rounded customer view, gather data from multiple sources like websites, apps, social media, emails, and in-store interactions. But collecting data is just the beginning. It's equally important to address quality issues early in the process. Salesforce Trailhead advises:
You should be scrupulous about addressing data quality issues as early as possible in the process. Make sure to address extremes, duplicates, outliers, and redundancy in CRM Analytics or other data preparation tools.
Avoid relying on proxy variables like ZIP codes or surnames, as these can inadvertently reflect biases tied to protected attributes. Instead, use pre-processing techniques like re-sampling to ensure datasets are balanced and representative. Regular evaluations of training data are also key to identifying and correcting biases.
Building Fair and Transparent AI Models
The way AI models are designed plays a huge role in their fairness. Adding fairness constraints during the development phase helps ensure algorithms treat all demographics equally. Additionally, using interpretable models allows you to understand and explain how AI makes decisions, rather than relying on "black-box" systems.
Testing models across different demographic groups is essential. Incorporating human oversight during this process can help identify and address any unintended biases before deployment.
Reva Schwartz, Principal Investigator for AI Bias at NIST, highlights the importance of diverse expertise:
It's important to bring in experts from various fields - not just engineering - and to listen to other organizations and communities about the impact of AI.
By involving diverse teams, businesses can uncover biases that might go unnoticed in more uniform groups. To ensure these measures stay effective, institutionalize oversight mechanisms that continually monitor and refine AI systems.
Governance and Oversight in AI-Powered Tools
Strong governance is essential for managing AI bias over time. The NIST AI Risk Management Framework offers guidance on embedding fairness and trust into every stage of AI development and deployment. Governance should be integrated throughout the process, helping to identify, measure, and address risks in your AI systems.
Set up AI review committees with members from varied departments and backgrounds to regularly audit AI decisions and documentation. For high-stakes decisions like loan approvals or pricing algorithms, human oversight is especially critical.
Community reviews can also provide valuable external insights and help identify blind spots. Additionally, empowering customers to control their data - by offering options to update or opt out of data collection - can improve trust and data accuracy.
Using Platforms with Built-In Bias Controls
Technology can support your efforts to reduce AI bias. Look for platforms designed with fairness in mind, offering features that make bias management easier.
For example, Inbox Agents (https://inboxagents.ai) includes tools to reduce bias in customer interactions. Its customizable business rules ensure consistent treatment across demographics, while auditing logs help identify and address bias patterns. Regular model retraining ensures the AI adapts to changes in your customer base and evolving fairness standards.
When choosing AI-powered tools for customer journey mapping, prioritize platforms that provide transparency, regular bias testing, and flexibility to adjust AI behavior. The right technology should help you manage bias effectively, not add complexity to the process.
Measuring the Results of Bias Reduction Efforts
To effectively reduce bias, it’s essential to measure the impact of your strategies on customer experiences and outcomes.
Tracking Fairness Metrics and Customer Outcomes
Begin by integrating fairness metrics into your evaluation process, alongside traditional business benchmarks. These metrics help identify disparities in outcomes across different demographic groups. For example, the EU's AI Act suggests keeping fairness metrics like demographic parity difference and equalized odds gap within a 10% range for high-risk models. In the U.S., the four-fifths (80%) rule sets a threshold for disparate impact ratios at 0.80 when comparing minority-to-majority outcomes, or 1.25 for majority-to-minority outcomes.
Pair these fairness metrics with customer-focused measures like satisfaction scores, Net Promoter Scores (NPS), and conversion rates. Research from McKinsey shows that improving customer journeys can boost satisfaction by 20%, increase revenue by 15%, and cut customer service costs by up to 20%. Meanwhile, Salesforce found that 88% of customers value their experience with a company as much as the products it offers.
To support these efforts, tools like IBM’s AI Fairness 360 toolkit, which was introduced in 2018, offer over 70 fairness metrics tailored to different business contexts. By choosing metrics that align with your organization’s goals and customer priorities, you can create a solid foundation for ongoing evaluation.
Continuous Monitoring and Bias Audits
Bias isn’t a static problem - it can develop over time as AI systems interact with new data and environments. That’s why one-time audits aren’t enough. Continuous monitoring is key, much like how system uptime is managed.
Set up real-time monitoring systems that track bias, data drift, and performance simultaneously. Automate bias detection with policies that send alerts when fairness thresholds are breached. This proactive approach helps you address potential issues before they negatively affect customers.
Bias can slip into any part of the data pipeline - whether during cleaning, transformation, enrichment, or feature engineering. Using data lineage tools allows you to trace the entire lifecycle of your data and pinpoint where bias originates, enabling more effective root-cause analysis. Regular audits that include cross-functional teams are also crucial for gathering diverse perspectives and ensuring a thorough review process.
This continuous vigilance ensures your AI systems remain compliant with evolving standards and deliver equitable outcomes.
Adapting to Changing Regulations and Expectations
AI regulations are evolving rapidly, and staying ahead of these changes is crucial. For instance, Colorado’s AI Act, signed in May 2024 and set to take effect in February 2026, requires risk assessments for high-impact AI systems. Similarly, the European Union's AI Act, enacted in mid-2024 and rolling out by 2026, mandates bias testing, documentation, and human oversight for high-risk AI systems.
Frameworks like the NIST AI Risk Management Framework can help you build trust into your AI processes. For generative AI, NIST-AI-600-1, released on July 26, 2024, outlines over 400 recommended actions for managing risks.
Customer expectations are also shifting. A survey revealed that 73% of customers expect brands to understand their needs. This means your bias reduction efforts must align not only with regulatory requirements but also with customer perceptions of fairness and respect. Regular feedback loops and external audits can help ensure you meet these rising expectations while maintaining trust and transparency.
Conclusion
AI bias in customer journey mapping can have far-reaching consequences, impacting brand reputation, eroding customer trust, and even reducing revenue. Beyond these challenges, biased systems can perpetuate discrimination against marginalized groups, including people of color, women, individuals with disabilities, and members of the LGBTQ community.
Addressing this issue calls for a focused, three-step approach: identifying the sources of bias, using high-quality data and transparent AI models to implement strategies, and conducting regular audits to monitor progress. These actions not only help avoid potential legal and financial troubles but also encourage diverse perspectives, resulting in products that cater to a broader audience's needs. This proactive approach lays the groundwork for sustainable growth.
Reducing bias isn’t just about correcting past mistakes - it’s also a smart business move. Companies that prioritize fairness in AI often experience tangible benefits, such as improved customer engagement, higher conversion rates, better retention, and increased customer lifetime value. Additionally, fostering fairness helps build trust within communities and creates collaborative environments that are better equipped to tackle societal challenges.
Platforms like Inbox Agents align with these principles by offering AI-powered tools designed with fairness in mind. Features such as personalized responses, automated message handling, and smart filtering ensure consistent and equitable treatment across all customer interactions. By unifying messaging channels, Inbox Agents helps brands deliver fair and inclusive experiences.
Creating trustworthy, bias-free AI in customer journeys is not just a goal - it’s a necessity for effectively serving a diverse and dynamic customer base.
FAQs
How does AI bias affect customer journey mapping, and how can businesses address it?
AI bias has the potential to disrupt customer journey mapping by producing insights that are skewed due to unbalanced or incomplete data. This can result in unfair or misleading portrayals of customer behaviors, preferences, or needs, which can negatively affect decision-making and ultimately harm customer satisfaction.
To combat AI bias, businesses need to take proactive steps. Start by auditing data and models to check for over- or under-representation of specific demographic groups. This involves creating datasets that are diverse and balanced, applying techniques like re-weighting or adversarial debiasing, and consistently monitoring model outputs for any signs of bias. Engaging a variety of perspectives - such as input from customers and cross-functional teams - during the review process can also help uncover hidden biases or assumptions.
Tools like Inbox Agents can support this effort with AI-powered features such as automated inbox summaries and smart replies. These tools can be fine-tuned with bias-checking mechanisms, enabling businesses to spot and address skewed patterns in customer interactions. This ensures a more accurate and fair representation of the customer journey, leading to better insights and decisions.
How does unchecked AI bias affect customer trust and brand reputation?
Unchecked AI bias can result in outcomes that feel unfair or inaccurate, potentially driving customers away and damaging your brand's reputation. This becomes even more pressing when such biases disproportionately affect marginalized groups, as it can give the impression of insensitivity or even discrimination.
The fallout from this can be severe - public criticism, eroded customer trust, and a decline in loyalty, all of which can hurt your business financially. Taking steps to identify and address AI bias early on is key to preserving trust and safeguarding your brand's image.
What steps can businesses take to ensure AI models are fair and unbiased?
To build AI models that are fair and unbiased, the first step is to carefully examine your training data. This means identifying and addressing any over- or under-representation of specific groups. Taking this step early helps you spot potential biases before the model is even created. Additionally, documenting the model’s purpose, data sources, and limitations - often done through a "model card" - adds a layer of transparency and accountability to the process.
As you develop the model, involve a diverse group of stakeholders, focus on selecting ethically appropriate variables, and emphasize principles like inclusiveness and explainability. Once the model is deployed, it’s crucial to keep an eye on its outputs. Regular monitoring can reveal any signs of bias, allowing you to adjust or retrain the model as needed. Automating this monitoring with tools that track performance and flag fairness issues can make it easier to stay aligned with changing data and regulations.
Equally important is fostering a culture of accountability within your organization. This involves bringing diverse perspectives into your team and implementing policies that encourage transparency and equitable results. By embedding these practices into your workflow, businesses can create AI systems that not only build trust but also contribute to a fairer customer experience.
