
Scoring Intent in Multilingual Conversations
AI-powered intent scoring helps businesses understand customer needs in multiple languages, like English and Spanish, by assigning confidence scores to messages. This ensures that urgent issues, such as refunds, are routed to the right teams quickly. Advanced systems combine message-level scoring with account-level insights, analyzing broader customer behavior to prioritize tasks effectively.
Key points:
- Confidence scores range from 0.0 (uncertain) to 1.0 (certain).
- Multilingual challenges include language switching, idioms, and tone differences.
- Specialized tools like Inbox Agents handle 150+ languages, unify messaging platforms, and prioritize high-value messages.
- AI techniques such as few-shot learning, zero-shot learning, and retrieval-augmented generation improve accuracy and scalability.
- Metrics like precision, recall, F1 score, and response time evaluate performance.
- Best practices address language nuances, minimize bias, and secure customer data.
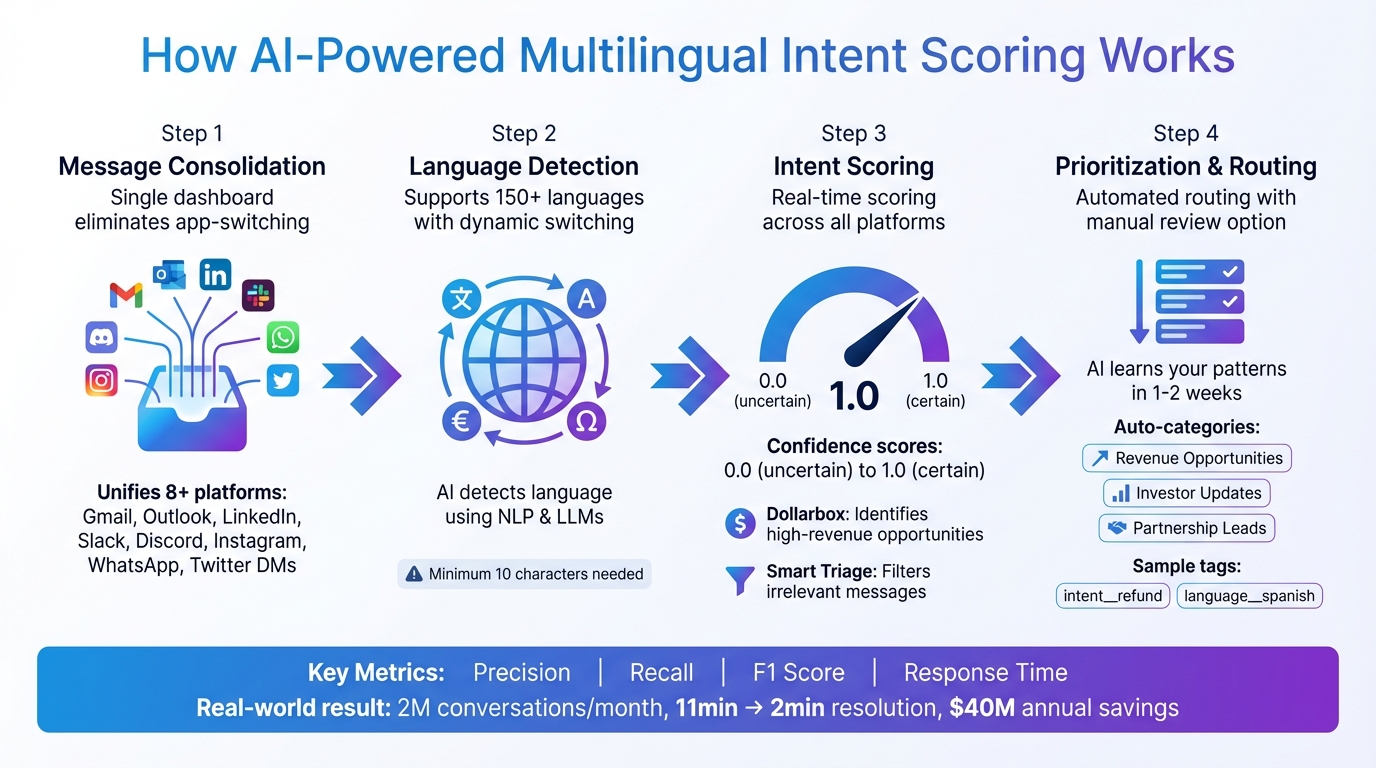
How AI-Powered Multilingual Intent Scoring Works: From Detection to Prioritization
Multilingual Evaluation of Generative AI (MEGA)
AI-Powered Intent Scoring Features in Inbox Agents
Inbox Agents brings together messages from Gmail, Outlook, LinkedIn, Slack, Discord, Instagram, WhatsApp, and Twitter DMs into a single platform. This eliminates the hassle of constantly switching between apps and allows users to handle conversations in multiple languages seamlessly. The platform’s AI analyzes every incoming message, detecting the language, assigning intent scores, and prioritizing tasks - all without requiring manual effort. This streamlined system lays the groundwork for real-time intent scoring, powered by advanced AI.
Multilingual Language Detection and Classification
With the help of natural language processing (NLP) and large language models (LLMs), Inbox Agents identifies the language of each message and assigns a confidence score. To ensure accuracy, the AI requires at least 10 characters of meaningful text. If the confidence level is uncertain, the system checks for manual language overrides or defaults to browser or workspace settings. This multi-step process ensures smooth communication, even when language detection isn’t straightforward.
The system also adapts dynamically as new messages arrive in a conversation, allowing it to adjust when customers switch languages mid-discussion. This adaptability improves how the platform handles multilingual interactions, keeping conversations efficient and effective.
Real-Time Intent Scoring Across Messaging Platforms
After identifying the language, Inbox Agents assigns intent scores across all connected messaging platforms at once. Features like Dollarbox stand out by pinpointing "hot opportunities" - messages with high revenue potential - in real time. At the same time, Smart Triage filters out irrelevant messages, ensuring that only the most critical ones are brought to your attention.
"The inbox identifies messages with revenue potential and puts it in one place." - Grace Annalise, Product Designer
The platform also offers Daily Briefings on Autopilot, automatically organizing messages by categories like Revenue Opportunities, Investor Updates, and Partnership Leads. For teams managing a flood of daily messages, this automated sorting is a game-changer, helping them focus on what truly matters without constant interruptions. By consolidating and scoring intent across various platforms, Inbox Agents ensures that urgent tasks rise to the top.
AI-Powered Personalization and Prioritization
Building on real-time scoring, the platform takes personalization to the next level by learning individual communication styles. Inbox Agents observes your unique patterns - such as preferred terminology, tone, and relationship dynamics - to improve its understanding of sender intent over time. Within just 1 to 2 weeks of regular use, the system achieves high accuracy in intent scoring. Users can speed up this learning process through the Priority Training feature, which lets them provide feedback on AI suggestions to fine-tune its performance.
Conversations are tagged by intent and language (e.g., intent__refund or language__spanish) to enable custom routing and prioritization. Additionally, high-value contacts can be flagged for manual review. The platform even includes AI-Powered Negotiation tools, capable of handling routine responses and scheduling meetings based on detected intent. Of course, these actions await your final approval before being sent out. This smart prioritization ensures you stay in control while saving time on repetitive tasks.
AI Techniques for Multilingual Intent Scoring
Inbox Agents employs advanced AI methods to deliver precise and scalable multilingual intent scoring. These techniques enable the platform to interpret customer intent across various languages without relying on massive training datasets. This allows the system to quickly adapt to new languages and contexts while maintaining high accuracy. Let’s dive into the core approaches that make this possible.
In-Context and Few-Shot Learning
Few-shot learning empowers intent classifiers to function effectively with just a handful of examples for each intent. This is especially useful when entering new markets or supporting less commonly spoken languages, where large datasets are often unavailable.
"The intent classifier can be trained with only a few examples per intent." - Rasa Documentation
In-context learning takes this a step further by incorporating similar examples directly into the model's prompt, enhancing its ability to make accurate predictions. For instance, Rasa’s LLM-based intent classifier typically includes 10 examples in its prompts to clarify tasks. Additionally, the LINGUIST method, using a 10-shot novel intent setup, demonstrated a notable improvement: +1.9 points in Intent Classification Recall and +2.5 points in Slot Tagging F1 Score compared to traditional methods. Instruction tuning on large multilingual models, like AlexaTM 5B, further boosts performance by generating high-quality annotated data, enabling effective zero-shot cross-lingual capabilities.
Few-shot learning tackles scenarios where data is limited, while zero-shot learning extends the AI’s reach to entirely new languages.
Zero-Shot Learning for Unseen Languages
Zero-shot learning allows the AI to process languages or intents it hasn’t encountered before by reframing intent detection as a Natural Language Inference (NLI) task. This approach evaluates whether a user’s input aligns with a candidate intent description, eliminating the need for costly manual annotations or translations for each new language.
For example, the Zero-Shot-BERT-Adapters (Z-BERT-A) model achieved impressive accuracy rates - 84.1% for Italian and 83.2% for German datasets - while utilizing only around 896,000 trainable parameters. Research also indicates that indexing queries from high-resource languages (like English, Chinese, Spanish, French, and Japanese) can deliver intent classification results for low-resource languages (such as Swahili, Urdu, and Indonesian) that are on par with indexing all available languages. Moreover, in zero-shot cross-lingual setups, instruction-tuned models outperformed machine translation baselines by +4.14 points on Slot Tagging F1 Score across six languages.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and Embeddings
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) combines neural information retrieval with text generation, allowing the AI to draw from external knowledge bases for accurate and fact-based responses. Embeddings, on the other hand, convert user queries and intent examples into numerical vectors, enabling semantic similarity searches even when exact keywords differ.
"Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) with large language models (LLMs) has demonstrated strong performance in multilingual question-answering (QA) tasks by leveraging relevant passages retrieved from corpora." - Jirui Qi, Raquel Fernández, and Arianna Bisazza
Multilingual embedding models map different languages into a shared vector space, making it possible to match a query in one language (e.g., German) with intent examples in another (e.g., English) without explicit translation. This reduces the likelihood of errors, such as the AI misinterpreting intent, by grounding predictions in retrieved examples. Additionally, configuring fallback intents ensures the system can handle cases where the predicted label doesn’t exist in the training data. By grounding intent scoring in retrieved data, these methods enhance Inbox Agents' ability to prioritize customer interactions effectively.
sbb-itb-fd3217b
Metrics for Evaluating Multilingual Intent Scoring
When evaluating multilingual intent scoring, it’s crucial to rely on metrics that assess both accuracy and overall business impact. These metrics shine a light on how well the system captures critical customer requests and ensures the reliability of automated responses. Beyond just validating the AI's performance, they also guide strategic decisions across multiple languages.
Accuracy, Precision, and Recall
Accuracy calculates the percentage of correct classifications - both positive and negative - out of the total. While it offers a general view of model performance, it can be misleading in multilingual setups where some intents are much more common than others. A model might appear accurate by focusing on frequent intents but still miss rare, high-priority requests.
Precision focuses on how often the system correctly identifies a specific intent when it makes a prediction. This metric is particularly important in scenarios where false positives carry a high cost, such as mislabeling a customer inquiry, which could lead to missed opportunities.
Recall, on the other hand, measures the percentage of actual intents that the system successfully identifies. It’s critical when failing to recognize a customer request is more damaging than an occasional misclassification. As Google for Developers explains, recall is key "when missing a positive instance is more costly than a false alarm".
F1 Score and Response Time
The F1 score - a balance of precision and recall - is especially valuable for datasets with uneven distributions of multilingual intents. It ensures that performance isn’t skewed by an overemphasis on precision or recall alone.
"The F1 score... balances the importance of precision and recall, and is preferable to accuracy for class-imbalanced datasets." - Google for Developers
This metric becomes even more critical when comparing performance across languages, ensuring the model doesn’t excel in a dominant language while underperforming in others.
Response time (or latency) measures how quickly the system processes input and delivers an output. As Shalini Harkar, Lead AI Advocate at IBM, points out, "minimizing latency is especially important in interactive and real-time programs". This metric is vital for maintaining smooth user experiences in live interactions.
Multilingual Performance Benchmarks
Industry benchmarks provide further insights into how multilingual intent scoring systems perform across different languages. For instance, in multi-turn evaluations, the o1-preview model achieved an average accuracy of 0.877 in the first turn but dropped to 0.707 by the third turn across all tested languages. Meanwhile, the Llama 3.1 405B model matched the third-turn accuracy of 0.707, outperforming o1-preview in Russian, while o1-preview excelled in Hindi, Chinese, and English.
Real-world use cases illustrate the practical benefits of these systems. In late 2024, a Swedish fintech company implemented confidence-based routing, which significantly improved efficiency. Their AI assistant handled over 2,000,000 conversations per month, automatically resolving interactions with over 90% confidence and routing those below 70% to human agents. This approach reduced average resolution times from 11 minutes to just 2 minutes, cut repeat inquiries by 25%, and saved an estimated $40 million annually.
However, these benchmarks also highlight areas for improvement. Performance in non-Latin scripts like Hindi, Russian, and Chinese often lags behind English, underscoring the need for further optimization to achieve truly global scalability.
Challenges and Best Practices in Multilingual Intent Scoring
Navigating multilingual intent scoring comes with its own set of hurdles, particularly when it comes to accuracy and building user trust. The main challenges stem from addressing cultural subtleties, minimizing bias, and ensuring the security of sensitive customer data. Tackling these challenges head-on is essential for creating systems that perform well across various markets.
Handling Cultural Nuances and Code-Switching
A straightforward translation often falls short of capturing the essence of idioms, humor, and regional quirks. Alix Gallardo, Co-Founder of Invent, explains it well:
"Translation changes words; localization adapts experiences, including humor, idioms, date/currency formats, so it feels native".
This distinction becomes even more vital in regions where users frequently switch between languages mid-conversation. For instance, systems must interpret each message's language independently, rather than sticking to one language for an entire session. To manage this effectively, AI models should dynamically adjust their tone and style based on the detected language and cultural context.
One way to address this is by programming the AI to confirm language switches explicitly (e.g., "You switched to French. Shall we continue in French?"). Additionally, testing with native speakers from target regions can help identify slang, idiomatic expressions, and common misspellings that automated tools often overlook. It's also crucial to differentiate between regional variations, such as Portuguese-Brazil and Portuguese-Portugal, by training models on region-specific data rather than relying on generic translations.
Reducing Bias in AI Models
Bias in multilingual intent scoring is another major challenge, often stemming from unbalanced training data, unclear algorithm designs, or biased user behavior patterns. For example, Amazon's now-discontinued AI hiring tool penalized resumes with terms like "women's" and favored those with masculine language because it was trained on data from a male-dominated industry. Similarly, in 2019, Apple's credit card algorithm faced scrutiny for offering women significantly lower credit limits than their husbands, despite similar financial profiles.
To mitigate bias, it's critical to develop fairness datasets that represent a wide range of cultures and languages, moving beyond Western-centric data. Regular monitoring and auditing of the model's behavior using context-sensitive metrics can help ensure fair performance across all demographic groups. Recruiting beta testers from target markets is another effective way to test for local variations and idiomatic usage. Zhaoming Liu from Shanghai University offers an insightful perspective:
"Cultural bias in LLMs is not solely a problem but also presents an opportunity. It can enhance our awareness and critical understanding of our own cultural biases while fostering curiosity and respect for diverse cultural perspectives".
Protecting Data Privacy and Security
While cultural and bias-related challenges are critical, safeguarding customer data is equally important. Using large language models (LLMs) for intent scoring often involves sending customer conversations to third-party APIs, which can pose privacy risks. It's essential for businesses to ensure compliance with data privacy standards and to clearly communicate how customer data is shared.
To protect against prompt injection attacks, it's recommended to map LLM outputs to predefined intent labels instead of returning raw generated text. As explained in the Rasa Documentation:
"The prompt used for classification won't be exposed to the user using prompt injection. This is because the generated response from the LLM is mapped to one of the existing intents, preventing any leakage".
Inbox Agents tackles these concerns with secure API connections and by ensuring system prompts don't inadvertently expose sensitive data. Additionally, enabling automatic language switching at both the agent and flow levels allows the model to respond in the user's preferred language without manual input, reducing the chances of misclassification and data vulnerabilities. These measures are key to maintaining both accuracy and trust in multilingual intent scoring systems.
Conclusion
AI-powered intent scoring is reshaping how businesses handle multilingual customer interactions. Instead of juggling multiple systems or relying on external translation services, companies can deploy a single intelligent agent that automatically identifies languages, adapts to regional nuances, and efficiently routes communications. This streamlined approach ensures operational efficiency while maintaining consistent quality across different markets.
AI translation is not only fast but also incredibly cost-efficient - up to 600 times cheaper than traditional human translation. Businesses can cut their translation budgets by as much as 80% by storing and reusing repetitive multilingual content. These tools also outperform manual methods by managing complex scenarios, such as mid-conversation language changes and enforcing local policies and formats.
For instance, Inbox Agents simplifies messaging by consolidating various channels into one platform. Its AI-driven capabilities include automated language detection, real-time translation for support teams, and personalized responses that maintain conversational flow - even when customers switch languages mid-discussion.
The real game-changer lies in moving beyond basic word-for-word translation. True localization addresses idioms, regional expectations, and subtle cultural nuances while preserving the original intent. As Ian Heinig from Sendbird aptly states:
"Since your business doesn't operate in one language, one policy, or one workflow, your AI support shouldn't either".
Building a scalable multilingual system starts with focusing on your top two or three audience languages, using fallback strategies, and consistently monitoring intent health. This approach ensures long-term success and adaptability.
With advanced AI models capable of understanding hundreds of languages and diverse intents, businesses are well-equipped to manage global customer conversations at scale. In today’s competitive global market, adopting AI-powered multilingual intent scoring isn’t just an option - it’s a necessity for staying ahead.
FAQs
How does AI handle intent scoring when customers switch languages during a conversation?
AI-powered intent scoring adjusts effortlessly to shifts in language by recognizing the change in real time and updating the conversation context accordingly. For example, if a customer switches languages mid-chat, the system quickly detects the new language, reinterprets the message, and recalculates intent scores - all without interrupting the natural flow of the conversation.
This precision is made possible by advanced multilingual models that leverage cross-lingual embeddings. These models ensure that intent detection stays accurate across different languages, preserving the conversation’s context and intent history even as the language evolves. Tools like Inbox Agents take this a step further by automatically identifying language changes, recalculating intent scores instantly, and responding in the customer’s current language. The result? Seamless, accurate communication that doesn’t require agents to step in for manual adjustments.
What are the advantages of using few-shot and zero-shot learning for multilingual intent scoring?
Few-shot learning makes it possible to train intent-scoring models using only a handful of labeled examples. This drastically cuts down the time and expense involved in preparing data. It’s an efficient approach, allowing models to be trained quickly with minimal resources. This makes it especially appealing for businesses that need to pivot swiftly to new markets or services. What’s more, few-shot techniques ensure consistent intent scoring across different languages, all while relying on the same small set of examples.
Zero-shot learning takes this concept even further by removing the need for task-specific training data altogether. Instead, it uses general-purpose training to classify user intents across various languages. This allows for quicker deployment and better support for languages that typically lack extensive resources. Together, these methods empower platforms like Inbox Agents to deliver precise, multilingual intent scoring, enabling businesses to meet customer needs in real time, no matter where they are in the world.
How does Inbox Agents protect data privacy and security in multilingual conversations?
Inbox Agents places a strong emphasis on protecting user data by following stringent privacy policies that align with key regulations like the California Online Privacy Protection Act (CalOPPA), Canada’s PIPEDA, and the EU’s privacy guidelines. This approach ensures that customer data is managed securely and meets legal standards across different regions.
Multilingual messages are handled exclusively within the Inbox Agents platform, eliminating the need for third-party tools. This approach significantly reduces the risk of data exposure. To further enhance security, the platform employs advanced encryption methods and strict access controls, keeping sensitive information safe during translation and analysis.
By integrating compliance with regulatory standards, secure internal processing, and powerful technical protections, Inbox Agents ensures customer intent is analyzed effectively without compromising the security or privacy of their data.
